




The Fight for Survival. The empire’s loss of territory was offset to a degree by consolidation and an increased uniformity of rule. The emperor Heraclius fully Hellenized the empire by making Greek the official language, thus ending the last remnants of Latin and ancient Roman tradition within the Empire.

Sortable list of Language names and two and three letter codes.
4 (Educational). Statutory language of provincial identity in Dagestan Autonomous Republic (1994, Constitution, Article 10).
Rus or RUS (Cyrillic: рус) may refer to:. Rus’ (name), the transliteration of the Slavic name for Ruthenia Rus’ (region), the associated territory Rus’ people, the people of Rus’
Russian thinkers most known in the West: Mikhail Bakunin, the man of anarchism. Leo Tolstoi, a great writer and a preacher of universal love
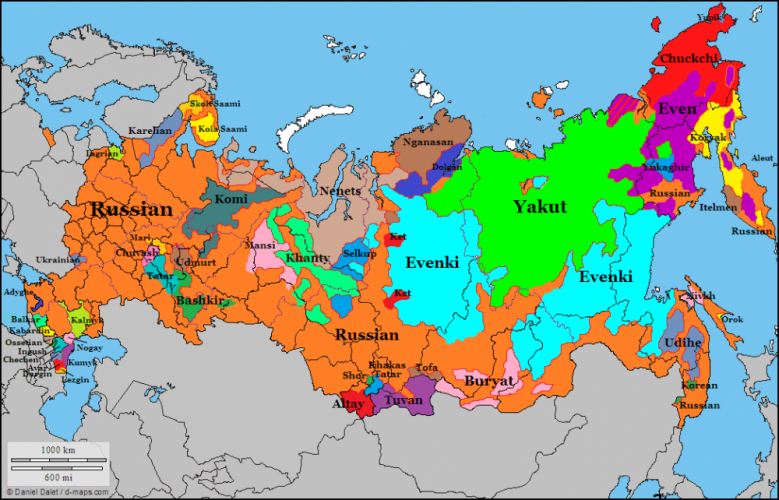

Listing of language information for Russian. 138,000,000 in Russian Federation (Arefyev 2012), all users. L1 users: 119,000,000 (Arefyev 2012).
Codes for languages associated with an item when the language code in field 008/35-37 of the record is insufficient to convey full information. Includes records for multilingual items, items that involve translation, and items where the medium of communication is a sign language. Sources of the
labor code of the russian federation of 31 december 2001 (federal law no. 197-fz of 2001)

Classification. Russian is an East Slavic language of the wider Indo-European family.It is a lineal [citation needed] descendant of the language used in Kievan Rus’, a loose conglomerate of East Slavic tribes from the late 9th to the mid 13th centuries.